Electrostatics Lab
Purpose
The goal of this experiment is to verify the inverse square nature of Coulomb’s Law and to determine the net amount of electrostatic charge on the test objects.
Materials
2 Ring stands
2 Red clamps
2 Nonmetallic pens or pencils (you supply)
2 Pith balls
Masking tape
Plastic pipe (CPVC)
Wool pad
Procedure
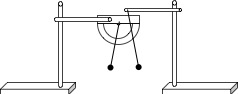
Use one red clamp to attach a pen or pencil (preferably wood or plastic) to a ring stand in order to make a horizontal support and hang one pith ball from the end using a very small piece of masking tape. Use another very small piece of tape to hang the other pith ball from the center of the protractor and attach it to the other ring stand with the other clamp. Important: With neither object charged there are two alignments to make. Adjust the heights so that the two balls hang at the same level. Also, adjust the protractor so that the second pith ball hangs at rest with the string vertical, aligned precisely at the 90° mark on the protractor. The protractor is used to measure the deviation from vertical for the second pith ball when the first pith ball is near.
1. Rub the CPVC pipe with wool pad and charge each pith ball. To the best of your ability try to “fully charge” each object to the maximum extent possible using this method.
2. Without delay (charge will dissipate over time), use the bases of the ring stands to bring the pith balls close to one another – close enough that the angle of deflection is apparent. Record the angle and the distance separating the two objects. It may be helpful to take a picture that can be scrutinized for this purpose.
3. Without changing the amount of charge on either object adjust the separation and note new values for angle and separation, repeating the process until you have a set of at least 5 trials.
4. Touch the pith balls with the ring stand or your hand to return them to a neutral, uncharged state. For the second data set, start by once again charging one of the pith balls to the greatest extent with the CPVC pipe. Then, instead of using the CPVC, allow the second pith ball to touch the first so that both are charged. This should result in the pith balls having a different amount of charge than in the first experiment.
5. Repeat the same procedure to obtain at least 5 trials with this different amount of charge.
6. Time permitting repeat the experiment with positively charged pith balls. Positive charge may be obtained either by induction using the CPVC or by conduction using a glass rod or other known positive source.
7. Important: measure and record the mass of the pith ball that hung from the protractor.
Analyses
1. For each data set create a graph of force vs. separation distance. All sets can be plotted on the same graph if you desire, provided there is a clear key or legend. For each experiment use a computer or calculator to determine the best fit using an inverse square model.
2. Use the blank column in the table to prepare calculated values based on the data that will result in a linear graph (but still based on the inverse square relation). Create a graph (or graphs) with linear regressions for all sets of data.
Questions
1. Show one example of any calculation(s) used in your analysis. At the very least this will include one example showing how you calculated force based on the measurements.
2. For each data set use a coefficient from a curve fit to determine a value for the amount of charge on each pith ball. Show all work. For each data set make the assumption that each ball has the same amount of charge.
3. Compare the amounts of charge found for the first experiment to the amounts found for the second experiment. Are these values consistent with what should be expected based on the procedure that was used? Justify your response.
4. Discuss error. Are the results consistent with Coulomb’s Law? What are indicators of error in the results and what are the most probable sources of error?
Complete report (40 pts):
§ Completed data table (10)
§ Force vs. Separation graph or graphs for all data sets, with regression equations (11)
§ Linearized versions of Force graphs with linear regressions (11)
§ Answers to questions on separate paper (8)
Data/Observations
Set 1 Charging method:
|
Pith ball mass = |
|
|
|
|
Separation ( ) |
Deflection Angle |
Force ( ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Set 2 Charging method:
|
Pith ball mass = |
|
|
|
|
Separation ( ) |
Deflection Angle |
Force ( ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Set 3 Charging method:
|
Pith ball mass = |
|
|
|
|
Separation ( ) |
Deflection Angle |
Force ( ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Set 4 Charging method:
|
Pith ball mass = |
|
|
|
|
Separation ( ) |
Deflection Angle |
Force ( ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|