AP Physics Lab – Projectile Motion
GENERAL OPERATION OF THE LAUNCHER:
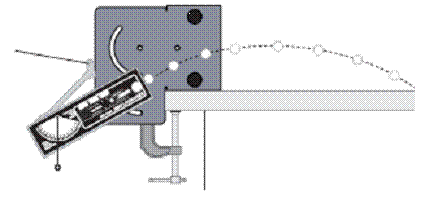
The PASCO mini launcher will be used for this experiment. Be sure to WEAR SAFETY GLASSES when operating this launcher or when others are operating this launcher. Be safe and always assume the barrel is loaded. Use a C clamp to fasten the launcher to the end of the table as shown below. Aiming is achieved by loosening the thumb screw and rotating the launcher to the desired angle above or below the horizontal as indicated by the plumb bob and protractor on the side of the launcher. When the angle has been selected, gently tighten the thumb screw. Do not over tighten or damage may occur to the ridges on the extruded barrel.
 |

THE EXPERIMENT:
The purpose of this experiment is to determine the muzzle velocity of the launcher and to test the validity of the parametric equations governing projectile motion.
Position: Velocity: Over Level Ground:
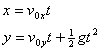
![]()
![]()
Part A
- Determining Muzzle Velocity and Predicting Maximum Height
1. Position and clamp the launcher to one end of the table, and adjust so that the ball will travel over the surface of the table and land on the tabletop. Assume that the ball lands at the same level as it is launched (and make sure that the launcher is arranged for this to happen).
2. Adjust the launcher to launch at an angle between 20° and 60° (but not 45°) above the horizontal. (See instructions for aiming given above.) Record the angle.
3. Loading the ball: Always cock the launcher with the ball already in the piston. Place the ball in the barrel. Push the ball down the barrel with the pushrod until the trigger catches the piston. One audible click indicates that the piston is cocked in the shortest range setting, two clicks indicate the medium range and three clicks set the piston in the long range position. For this experiment use the long range position.
4. Fire one shot to locate where the ball hits the table. At this position, use masking tape to attach a piece of construction paper to the table in such a manner that its length is parallel to the direction of the projectile’s motion. When the ball hits the paper it will leave a mark or indentation. Fire several shots, being careful not to change the aim of the launcher.
5. Measure the horizontal distance from the bottom of the ball as it leaves the barrel (this position is marked on the side of the barrel) to the point of impact. Record this distance – the horizontal distance (or range) traveled by the ball.
6. Find the mean of the range values. Record this information and proceed to calculate the initial speed (or muzzle speed) of the ball using the mean of the range and the angle of the launch. Show all work in the space provided.
7. Now use the initial velocity to calculate the maximum height attained by the ball in its flight. Record this calculated (theoretical) value. Again show work.
8. Set up a hoop at this same height and position it at the midpoint of the ball’s trajectory. Launch the ball and observe its motion (hopefully) through the hoop. If it does not go through the hoop adjust the position until it does so. Use the hoop as a means to judge the actual maximum height of the ball. Record this observed value.
9. Repeat steps 2 through 8 for two more angles: the compliment of the first angle you used and 45°. Note: the observed range of the complimentary angle may or may not be the same as the first trial.
Part B – Range and Time of Projectile Launched at an Angle Over Uneven Terrain
1. Rearrange the launcher to fire from the table’s edge so that the ball will land on the floor. Choose a convenient angle for launching.
2. Measure the vertical distance from the bottom of the ball as it leaves the barrel (this position is marked on the side of the barrel) to the floor. Record this distance – the vertical component of displacement between launch and impact.
3. Use the mean value of the muzzle speed found in part A along with the angle of the launcher and the vertical displacement to calculate a predicted range and time in the air. (i.e. use physics to predict where and when the ball will land on the floor)
4. Just for FUN: place a cup or other small container at the predicted range and see if you can “get a basket” on the first shot.
5. After the FUN: make several shots without the cup and measure and record the actual range of the projectile by its impact on a paper target taped to the floor. Also, use a stopwatch to measure the time in the air. Repeat several times to get an average value for each.
6. Repeat this experiment at least once with a different launch angle.
Questions
1. Determine the mean percent error in each calculated value for maximum height, assuming the observed value is the “true” maximum height.
2. Determine the percent error in each calculated time of flight, assuming the observed mean value is the “true” time of flight.
3. Determine the percent error in each calculated range, assuming the observed mean value is the “true” range.
4. Discuss the variation in the values for the muzzle speed – other than error, what may be the cause(s) of this variation?
5. How well do you think the results of this experiment support the equations and concepts of projectile motion? Explain and support your answer.
6. Discuss error. What are the signs and indications that error occurred? What are the most like sources of those errors that are evident? Remember to consider both random and systematic error.
Data/Calculations – Part A
|
Launch Angle |
Range |
Muzzle Speed |
Max. Height (Calculated) |
Max. Height (Observed) |
|
|
Trial 1 |
|
|
|
|
Trial 2 |
||||
|
Trial 3 |
||||
|
Mean |
||||
|
|
Trial 1 |
|
|
|
|
Trial 2 |
||||
|
Trial 3 |
||||
|
Mean |
||||
|
|
Trial 1 |
|
|
|
|
Trial 2 |
||||
|
Trial 3 |
||||
|
Mean |
In the space below show the calculations of muzzle speed and maximum height for at least one of the rows in the table.
Data/Calculations – Part B
Mean Muzzle Speed (Part A): _____________
Vertical Displacement: _____________
|
Launch Angle |
Time of Flight (Calculated) |
Time of Flight (Observed) |
Range (Calculated) |
Range |
|
|
|
Trial 1 |
|
Trial 1 |
|
Trial 2 |
Trial 2 |
|||
|
Trial 3 |
Trial 3 |
|||
|
Mean |
Mean |
|||
|
|
|
Trial 1 |
|
Trial 1 |
|
Trial 2 |
Trial 2 |
|||
|
Trial 3 |
Trial 3 |
|||
|
Mean |
Mean |
|||
|
|
|
Trial 1 |
|
Trial 1 |
|
Trial 2 |
Trial 2 |
|||
|
Trial 3 |
Trial 3 |
|||
|
Mean |
Mean |
In the space below show the calculations of time and range for at least one of the rows in the table.